Batzen. Part 12
Description
This section is from the "Encyclopedia Of Practical Receipts And Processes" book, by William B. Dick. Also available from Amazon: Dick's encyclopedia of practical receipts and processes.
Batzen. Part 12
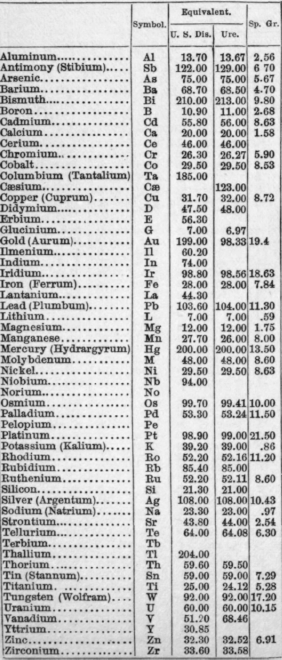
6150. Table of Symbols and Equivalents of Metallic Elements
6150. Table of Symbols and Equivalents of Metallic Elements. The specific gravity of the following are given at water standard. The equivalents are multiples,of hydrogen, which is adopted as the basis, or 1.
6151. Table of Symbols and Equivalents of Non-Metallic Elements
6151. Table of Symbols and Equivalents of Non-Metallic Elements. The specific gravity of these are given in their gaseous form, air being the standard or 1.000. The equivalents are multiples of hydrogen which is adopted as the basis or 1.
Symbol. | Equivalent. U. S. Dis. Ure. | Specific Gravity. | ||
Bromine | Br | 78.4 | 80.0 | 5.4110 |
Carbon | C | 6.0 | 6.0 | .8290 |
Chlorine | C1 | 35.5 | 35.5 | 2.4530 |
Fluorine | F1 | 18.7 | 19.0 | 1.3270 |
Hydrogen | H | 1.0 | 1.0 | .0692 |
Iodine | 1 | 126.3 | 127.0 | •8.7827 |
Nitrogen | N | 14.0 | 14.0 | .9713 |
Oxygen | 0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 1.1056 |
Phosphorus | P | 32.0 | 32.0 | 4.2840 |
Selenium | Se | 40.0 | 40.0 | 7.6960 |
Sulphur. | S | 16.0 | 16.0 | 2.2140 |
6152. To Reduce Parts by Volume or Measure to Parts by Weight
6152. To Reduce Parts by Volume or Measure to Parts by Weight. Multiply the parts by volume or measure by the specific gravity of the different substances; the result will be parts by weight.
6153. To Find the Length of the Day or Night
6153. To Find the Length of the Day or Night. To find the length of any day, double the time of sunset. Double the hour of sunrise will be the length of the night.
Continue to:


