Mechanical Tissues. Part 5
Description
This section is from the "Histology of Medicinal Plants" book, by William Mansfield. Also see Amazon: Histology of Medicinal Plants.
Mechanical Tissues. Part 5
Endodermal Cells
The endodermal cells of the different plants vary greatly in form, color, structure, and composition of the wall, yet these different endodermal cells may be divided into two groups: first, thin-walled parenchyma-like cells, and, secondly, thick-walled fibre-like cells. In the thin-walled endodermal cells the walls are composed of cellulose, and the cell terminations are blunt or rounded. When the drug is powdered the cells break up into small diagnostic fragments. In the thick-walled endodermal cells the walls are lignified and porous, and the ends of the cell are frequently pointed and resemble fibres.
Sarsaparilla root, triticum, convallaria, and aletris have thick-walled endodermal cells.
Structure Of Endodermal Cells
The endodermal cells of sarsaparilla root (Plate 35, Fig. 1) are never more than one layer in thickness. The walls are porous and of a yellowish-brown color. Alternating with the thick-walled cell is a thin-walled cell, which is frequently referred to as a passage cell.
The endodermal cells of triticum (Plate 35, Fig. 2) are yellowish and the walls are porous and striated. There are one or two layers of cells. The cells forming the outer layer have very thin outer but thick inner walls, while the cells forming the inner layer are more uniform in thickness.
The endodermal cells of convallaria (Plate 35, Fig. 3) are yellowish white in color, and the walls are porous and striated.
The outer wall of the layer of cells is thinner than the inner wall. The innermost layer of cell is more uniformly thickened.
The endodermal cells of aletris (Plate 35, Fig. 4) are yellowish brown, slightly porous and striated. There are one or two layers of these cells, and two of the smaller cells usually occupy a space similar to that occupied by the radically elongated single cell.
On longitudinal view the endodermal cells of sarsaparilla triticum, convallaria, and aletris appear as follows:
Those of sarsaparilla (Plate 36, Fig. 1) are greatly elongated, the ends of the cells are blunt or slightly pointed, and the walls appear porous and striated.
Those of triticum (Plate 36, Fig. 2) are elongated, the walls are porous and striated, and the outer wall is much thinner than the inner wall. The end wall between two cells frequently appears common to the two cells.
Those of convallaria (Plate 36, Fig. 3) are elongated, and the end wall is usually blunt. The outer wall is thinner than the inner wall.
Those of aletris (Plate 36, Fig. 4) are fibre-like in appearance; the ends of the cells are pointed and the wall is strongly porous. The longitudinal view of these cells is shown in plate 36.
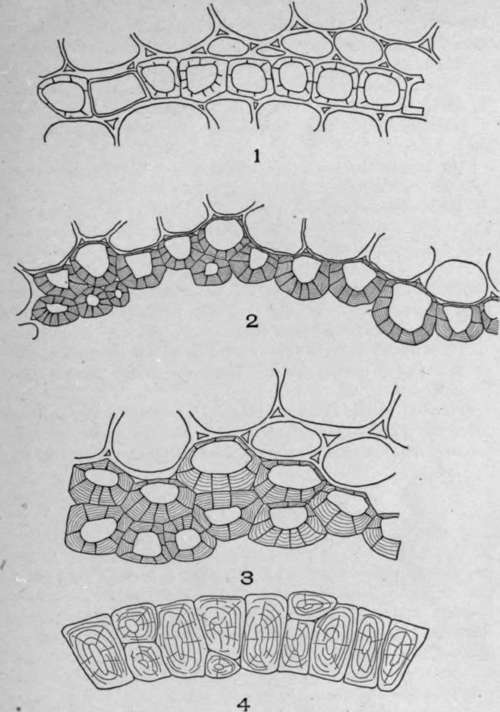
Plate 35. Cross-Sections of Endodermal Cells of:
1. Sarsaparilla root (Smilax officinalis, Kunth).
2. Triticum {Agropyron repens, L.).
3. Convallaria (Convallaria majalis, L.)
4. Aletris (Aletris farinosa, L.).
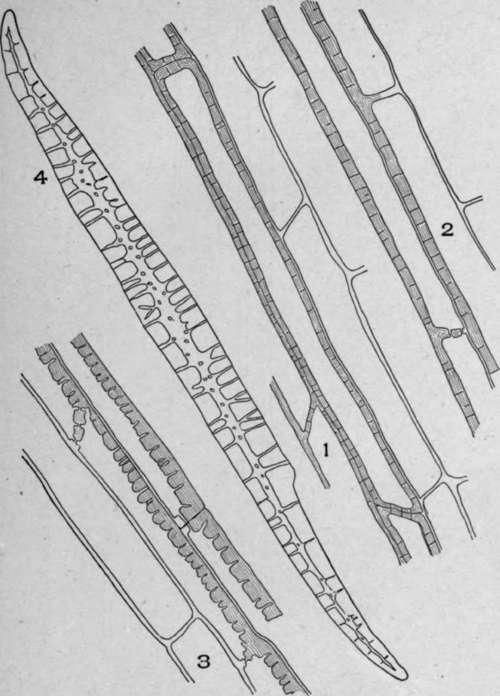
Plate 36. Longitudinal Sections of Endodermal Cells.
1. Sarsaparilla root (Smilax officinalis, Kunth).
2. Triticum (Agropyron repens, L.).
3. Convallaria (Convallaria majalis, L.).
4. Aletris (Aletris farinosa, L.).
Hypodermal Cells
Hypodermal cells occur in sarsaparilla root and in triticum. In the cross-section of sarsaparilla root (Plate 37, Fig. 1) the hypodermal cells are yellowish or yellowish brown. The outer wall is thicker than the inner wall, the cell cavity is mostly rounded, and contains air. The walls are porous and finely striated. On longitudinal view the hypodermal cells of sarsaparilla (Plate 37, Fig. 2) are greatly elongated; the outer and side walls are thicker than the inner walls. The ends of the cells are blunt and distinct from each other.
In cross-section the hypodermal cells of triticum (Plate 37, Fig. 3) are nearly rounded in outline, and the walls are of nearly uniform thickness. In longitudinal view (Plate 37, Fig. 4) the same cells appear parenchyma-like, and the walls between any two cells appear common to the two cells.
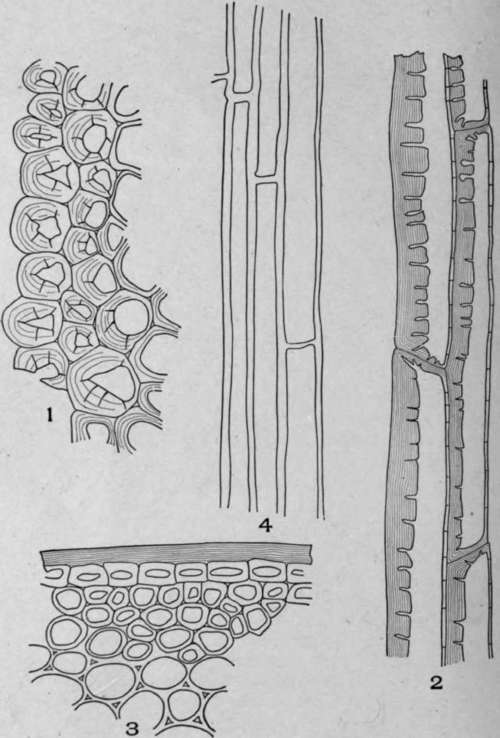
Plate 37. Hypodermal Cells.
1. Cross-section sarsaparilla root (Smilex officinalis, Kunth).
2. Longitudinal section sarsaparilla root (Smilax officinalis, Kunth).
3. Cross-section triticum (Agropyron repens, L.).
4. Longitudinal section triticum (Agropyron repens, L.).
Continue to:


