Drawing And Its Utility. Part 7
Description
This section is from the book "Carpentry for Boys", by J. S. Zerbe. Also available from Amazon: Carpentry for Boys.
Drawing And Its Utility. Part 7
Definitions
The following figures show the various geometrical forms and their definitions:
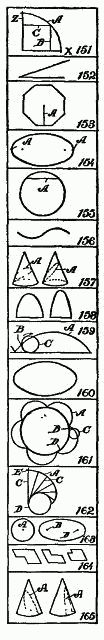
151. Abscissa. - The point in a curve, A, which is referred to by certain lines, such as B, which extend out from an axis, X, or the ordinate line Z.
152. Angle. - The inclosed space near the point where two lines meet.
153. Apothegm. - The perpendicular line A from the center to one side of a regular polygon. It represents the radial line of a polygon the same as the radius represents half the diameter of a circle.
154. Apsides or Apsis. - One of two points, A, A, of an orbit, oval or ellipse farthest from the axis, or the two small dots.
155. Chord. - A right line, as A, uniting the extremities of the arc of a circle or a curve.
156. Convolute (see also Involute). - Usually employed to designate a wave or folds in opposite directions. A double involute.
157. Conic Section. - Having the form of or resembling a cone. Formed by cutting off a cone at any angle. See line A.
158. Conoid. - Anything that has a form resembling that of a cone.
159. Cycloid. - A curve, A, generated by a point, B, in the plane of a circle or wheel, C, when the wheel is rolled along a straight line.
160. Ellipsoid. - A solid, all plane sections of which are ellipses or circles.
161. Epicycloid. - A curve, A, traced by a point, B, in the circumference of a wheel, C, which rolls on the convex side of a fixed circle, D.
162. Evolute. - A curve, A, from which another curve, like B, on each of the inner ends of the lines C is made. D is a spool, and the lines C represent a thread at different positions. The thread has a marker, E, so that when the thread is wound on the spool the marker E makes the evolute line A.
163. Focus. - The center, A, of a circle; also one of the two centering points, B, of an ellipse or an oval.
164. Gnome. - The space included between the boundary lines of two similar parallelograms, the one within the other, with an angle in common.
165. Hyperbola. - A curve, A, formed by the section of a cone. If the cone is cut off vertically on the dotted line, A, the curve is a hyperbola. See Parabola.
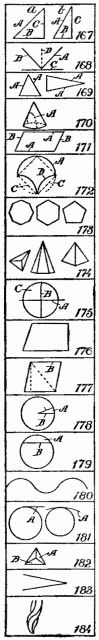
167. Hypothenuse. - The side, A, of a right-angled triangle which is opposite to the right angle B, C. A, regular triangle; C, irregular triangle.
168. Incidence. - The angle, A, which is the same angle as, for instance, a ray of light, B, which falls on a mirror, C. The line D is the perpendicular.
169. Isosceles Triangle. - Having two sides or legs, A, A, that are equal.
170. Parabola. - One of the conic sections formed by cutting of a cone so that the cut line, A, is not vertical. See Hyperbola where the cut line is vertical.
171. Parallelogram. - A right-lined quadrilateral figure, whose opposite sides, A, A, or B, B, are parallel and consequently equal.
172. Pelecoid. - A figure, somewhat hatchet-shaped, bounded by a semicircle, A, and two inverted quadrants, and equal to a square, C.
173. Polygons. - Many-sided and many with angles.
174. Pyramid. - A solid structure generally with a square base and having its sides meeting in an apex or peak. The peak is the vertex.
175. Quadrant. - The quarter of a circle or of the circumference of a circle. A horizontal line, A, and a vertical line, B, make the four quadrants, like C.
176. Quadrilateral. - A plane figure having four sides, and consequently four angles. Any figure formed by four lines.
177. Rhomb. - An equilateral parallelogram or a quadrilateral figure whose sides are equal and the opposite sides, B, B, parallel.
178. Sector. - A part, A, of a circle formed by two radial lines, B, B, and bounded at the end by a curve.
179. Segment. - A part, A, cut from a circle by a straight line, B. The straight line, B, is the chord or the segmental line.
180. Sinusoid. - A wave-like form. It may be regular or irregular.
181. Tangent. - A line, A, running out from the curve at right angles from a radial line.
182. Tetrahedron. - A solid figure enclosed or bounded by four triangles, like A or B. A plain pyramid is bounded by five triangles.
183. Vertex. - The meeting point, A, of two or more lines.
184. Volute. - A spiral scroll, used largely in architecture, which forms one of the chief features of the Ionic capital.
Continue to:


