Thymus. Thyme
Description
This section is from the book "A Manual of Materia Medica and Pharmacology", by David M. R. Culbreth. Also available from Amazon: Manual of Materia Medica and Pharmacology.
Thymus. Thyme
Oleum Thymi. Oil of Thyme, official.
Thymus vulgaris,
Linne.
A volatile oil distilled from the flowering plant, containing 20 p. c, by volume, of phenols.
Habitat. S. Europe (Portugal to Greece); cultivated in gardens, etc. Syn. Common Garden Thyme, Mother of Thyme; 01. Thymi, Thyme Oil; Fr. Thym; Essence de Thym; Ger. Herba Thymi, Thymian; Thymianol. Thy'mus. L. fr. Gr.
strength, its invigorating smell. Used in temples as incense.
Vul-ga'ris. L. ordinary, common - i. e., the kind growing wild and in common use.
Plant. - Small shrub, 25-30 Cm. (10-12') high; stem and branches quadrangular; bark pale brown, shoots purplish; leaves 6-12 Mm. (1/4-1/2') long, oval, blunt, entire, margin revolute, thick, smooth, dotted with many oil-glands, paler, pubescent beneath; flowers June-July, polygamous, cymes, forming capitate heads, pale purple. Entire plant aromatic, peculiarly attractive to bees, flies, etc.
Constituents. - Volatile oil 2.5 p. c. (thymol), resin, tannin, gum.
Oleum Thymi. Oil of Thyme. - This volatile oil is a colorless, red liquid, characteristic odor and taste, darker and thicker with age, soluble in 2 vols. of 80 p. c. alcohol, sp. gr. 0.912, laevorotatory; contains at least 20 p. c, by volume, of phenols, also cymene, C10H14, l-pinene, borneol, linalool; the phenol content in the French and German oil, amounting to 25-42 p. c, is mostly thymol, but sometimes carvacrol, or a mixture of the two, whereas in the Spanish oil it is chiefly carvacrol, amounting to 50-70 p. c. Test: 1. Shake 1 Ml. (Cc.) with hot distilled water 10 Ml. (Cc), cool, pass aqueous layer through a wetted filter - filtrate not blue or violet with a drop of ferric chloride T. S. Should be kept cool, dark, in well-stoppered, amber-colored bottles. Dose, ej-5 (.06-.3 Ml. (Cc.)).
Adulterations. - Oil of turpentine, which lowers specific gravity, increases angle of rotation; wild thyme oil only increases angle of rotation.
Thymol. Thymol, C10H14O, official. - (Syn., Acidum Thymicum, Thymic Acid, Methyl-propyl phenol; Fr. Acide Thymique; Ger. Thymolum, Thymiansaure.) This phenol (monotomic) occurs in the volatile oil of T. vulgaris, and some other volatile oils, especially Monarda punctata, and Ptycho'tis Cop'tica (Ajowan - Umbelliferae), the latter alone supplying most of the commercial article. It is obtained from any of these oils by distillation at 200° C. (392° F.), the more fluid distillate (hydrocarbons) being saved for various purposes, and the residue subjected to freezing, whereby thymol crystallizes out; or may agitate this residue with sodium hydroxide solution, and after a time add hot water to separate sodium-thymol (NaC10H13O) solution from thymene and to allow the unattacked oil to float on top; to sodium hydroxide solution add hydrochloric acid, which sets thymol free; purify by distillation and crystallization, decolorizing, if necessary, with animal charcoal; yield 20-61 p. c. It is in large colorless, translucent, rhombic prisms, aromatic, thymelike odor, pungent, aromatic taste, very slight caustic effect upon the lips; soluble in glacial acetic acid, fixed or volatile oils, water (1010),
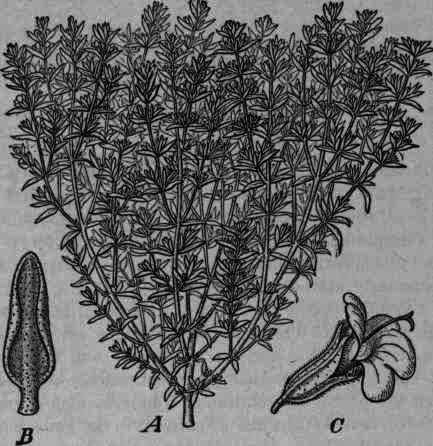
Fig. 327. - Thymus vulgaris: A, plant in bloom: B, leaf seen from under surface, magnified 4 diam.; C, flower seen from the side, magnified 5 diam.
alcohol (1), chloroform (.7), ether (1.5), olive oil (1.7); alcoholic solution (1 in 20) neutral, optically inactive; isomeric with carvone (carvol, carvacrol); as a solid heavier than water, when liquefied by fusion lighter than water, melts at 50° C. (122° F.); liquefies when triturated with equal weight of camphor or menthol. Tests: 1. Dissolve a small crystal in glacial acetic acid 1 Ml. (Cc.), add sulphuric acid 6 drops and nitric acid 1 drop - liquid deep bluish-green by reflected light. 2. Heat 1 Gm. with 5 Ml. (Cc.) of a 10 p. c. solution of sodium hydroxide - clear, colorless, or pale red solution, darker on standing, without separating oily drops; add few drops of chloroform, agitate - violet color; volatilize 2 Gm. on water-bath - residue .05 p. c. 3. Alcoholic solution (1 in 20), + ferric chloride T. S. - not violet (abs. of phenol). Impurities: Phenol, etc. Should be kept in well-closed containers. Dose, antiseptic, gr. 1-5 (.06-.3 6m.); anthelmintic, gr. 15 (1 Gm.), per die.
Unoff. Preps.: Oil: Capsules, Pills.; Thymol: Solution, for antiseptic spray (1 to 1000), Nebula Thymolis, 1 p. c, + light liquid petrolatum 100. Ointment, 1-5 p. c. Inhalation, 1 gr. (.06 Gm.) to each. Antiseptic Fluid, 1 p. c. Plant: Fluidextract (glycerin 10, alcohol 25, water 65); dose, exv-60 (1-4 Ml. (Cc.)).
Properties. - 1. Oil: Stimulant, tonic, emmenagogue, antispasmodic. If excessive doses given, have vomiting, depression, coldness, death by exhaustion, increased urine, which acquires green color and violet odor. II. Thymol: Stimulant, antiseptic, deodorant, disinfectant, parasiticide, antipyretic, local anaesthetic. Its action stands between phenol and oil of turpentine, being 10 times less poisonous than the former, yet a far more powerful and permanent antiseptic; it is anaesthetic to the skin and mucous membranes, paralyzing the ends of sensory nerves; it is eliminated by breath and urine.
Uses. - I. Oil: Chlorosis, rheumatism, neuralgia, bronchitis, diarrhoea, gleet, gonorrhoea, leucorrhoea, vesical catarrh; externally in baths, lotions for scabies, muscular rheumatism, to correct fetor from sores, ulcers, gangrene. Applied to cotton for toothache, earache, for veterinary practice, scenting soap. II. Thymol: Precisely like the oil, not much internally - anthelmintic, etc., but externally as an antiseptic in surgery, to lessen fetor from sores, ulcers, gangrene, in stomatitis, diphtheria, fetid bronchitis, coryza, rhinitis, ozaena, conjunctivitis, otorrhoea, gonorrhoea, uterine lochia, cancer, leucorrhoea, warts, skin diseases (psoriasis, eczema, etc.), diarrhoea, dysentery, typhoid fever, diabetes. A good dressing is thymol 1 Gm., alcohol 10 Ml. (Cc), glycerin 30, water q. s. 1,000 Ml. (Cc). Flies are fond of and often become attracted by it, which is its only objection.
Thymacetin, C6H2.CH3OC2H5C3H7NH.COCH3, a derivative, has the same relation to thymol that phenacetin has to phenol, and is prepared similarly; it is a white crystalline powder, soluble in alcohol, slightly in water. Analgesic, hypnotic, antiseptic; used in neuralgic headache like phenacetin. Dose, gr. 5-15 (.3-1 Gm.).
Thyme plant (fresh) is used as a condiment to aid digestion of fat pork, goose, duck, etc., and to flavor insipid dishes, as is sage, marjoram, parsley; it is used also with other aromatic herbs in baths, cataplasms, fomentations, for rheumatism, gout, scabies, indolent ulcers.
Allied Plants:
Continue to:


